
Wood Pellet Quality Standards in Europe
Europe is the most important market for wood pellet products, in order to give the users a clear quality classification of wood pellet products, many European countries established their national wood pellet quality standards to regulate the wood pellet quality, for instance Austria, Germany, France, Italy, etc. To have an clear knowledge about the European wood pellet standards is very important for every wood pellet plant. The majority of the world wood pellets are sold to the European countries. Also, as the pioneer of the utilization of wood pellet fuel, Europe is at a superior position of establishing the wood pellet standards, and many other countries are willing to adapted to the European wood pellet standards.
Although, there are several national pellet standards have been issued, the specified parameters of the wood pellet products are differ among the different national standards. Take the raw materials for wood pellet as an example, according to the Austrian standard ÖNORM M 1735, the wood pellet can only be manufactured from natural wood and bark, which you can find a similar regulation in the Germany wood pellet standard DIN plus. But the wood pellet raw materials according to the Swedish standard SS 187120 are normally logging and cutting residues, by-products from forest and timber industries, straw and paper. But in the Germany standard DIN 51731, the wood pellet can be produced only by the wood in natural state which had only been treated mechanically. The specified regulation of the national wood pellet standards are various, and there is no agreement about which national wood pellet standard is the best. On one hand, the variety of wood pellet standards increase the difficulty for wood pellet manufacturers and make it hard for the users to choose which kinds of wood pellet they should use. On the other hand, the variety of wood pellet standards also prevent the regional and international exchange of wood pellets.
Therefore, the Europe Pellet Council decided to release a pellet products standard (EN 14961 – 2) based on the other wood pellet national standards. The EN pellet standard is aimed to improve the chaotic wood pellet standards system. This EN pellet standard is in force, all the national pellet standards in Europe have to be withdrawn or adapted the EN pellet standard in six months. The EN pellet standard classified the wood pellet into three levels, A1, A2, and B. About the raw materials for EN standard wood pellets, A1 wood pellets are made from stemwood, chemically untreated wood residues; A2 wood pellets are manufactured by whole trees without roots, stemwood, logging residues, bark, chemically untreated wood residues; B wood pellets are produced by forest, plantation and other virgin wood, by-products and residues from wood processing industry and used wood. Below there is a picture which can help you compare the different wood pellet standards in Europe.
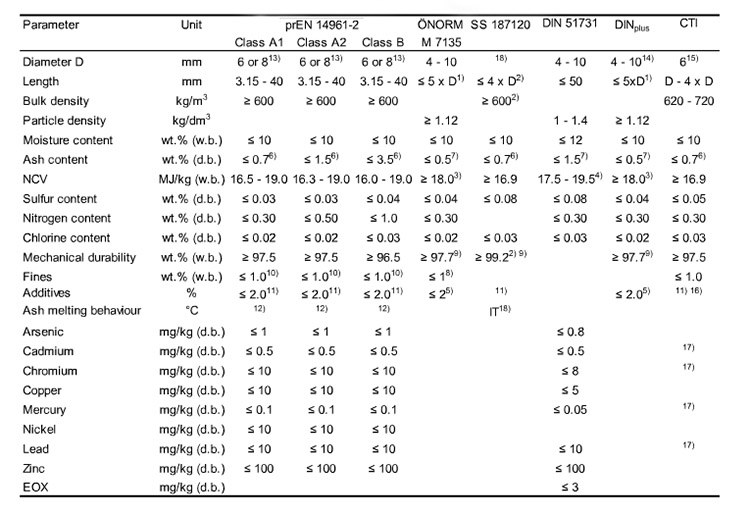
Wood Pellet Analysis Standards in Europe
Wood pellet standards is not only a batch of technical requirements of the pellet fuel, it also contains a series of test specifications for the pellet fuel with different parameters. Though each pellet standard has its own physical and chemical analysis standard, they will not be mentioned here as they are adapted the EN standard.
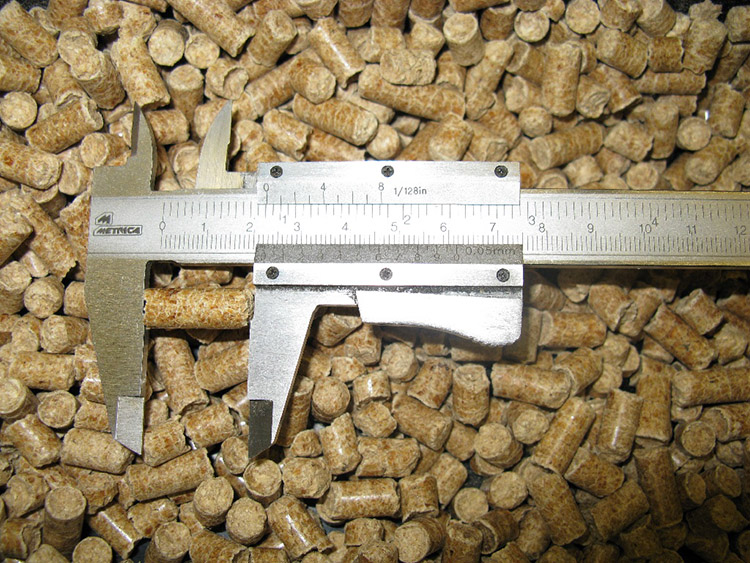
Length and diameter
The length and diameter measurement standard is under development. In this section, the inspectors do the measurement test manually with a caliper. They will measure each pellet of the test portion individually. In the test report, the length of the wood pellets will be recorded separately according to the different diameters of the wood pellet, such as 6mm, 8mm and 10mm. The proportion of wood pellets under 40mm, the proportion of wood pellets between 40mm and 45mm, the proportion of overlong wood pellets over 45mm and the proportion of broken wood pellets will be mentioned in the test report. All the statistics is mentioned by weight.
Bulk density
The bulk density is measured by a standardized container. The standardized container has a specified volume, exactly 5 litre of wood pellets. The bulk density measurement can be divided into three steps. Firstly, the container will be filled with wood pellets. Then, the container will fall three times from the height of 15cm. Finally, the bulk density will be measured and recorded.
Moisture content
In EN 14774-1, the moisture content of wood pellets is determined. During the test, at least a 300 gram wood pellet sample must be provided, and the inspectors will dry the wood pellets at a temperature about 105℃.
Ash content
According to EN 14775, the ash content must be determined at the temperature of 550℃. This requirement is largely different from the Austrian and German pellet standards, as they require a measure temperature of 850℃. But the required temperature, 850℃ is too high as the volatile substances in the wood pellets already volatilize into the gaseous phase, hence, the result of the test is influenced by the situation.
Mechanical durability
The mechanical durability is mainly determined by the standard EN 15210-1, and the specialized tester is widely used. Except, there are some other testers which have been widely used in recent years, such as the Ligno – Tester. This piece of equipment is adopted from the Austrian and German pellet standard. The equipment to test the abrasion of wood pellet is borrowed from the Swedish wood pellet standard, which is a hexagonal rotating drum.
The tester for mechanical durability of wood pellet
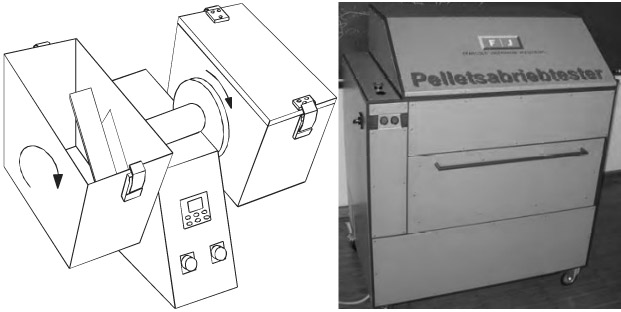
The ligno-tester

The tester for abrasion of wood pellet
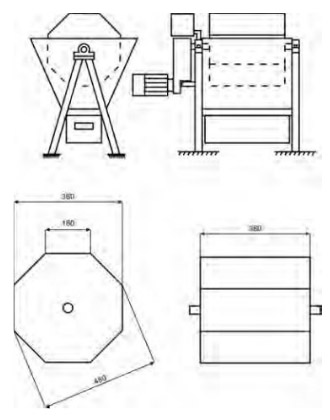
Conclusion
As the rapid development of wood pellet market, there are multiple wood pellet standard systems in the world. The two largest wood pellet standards that are widely used in the world are the EN pellet standard and the ISO pellet standard. Also, the European pellet council developed the wood pellet certification system ENplus, which can be applied by any wood pellet plant in the world. It helps to defined the quality of the wood pellet of the wood pellet plant, therefore the customers can easily find out the wood pellet they need. The ISO 238/TC solid biofuels is established in 2007, and has been regularly upgraded ever since. It is a complete wood pellet quality system which includes six parts: terminology, fuel specifications and classes, quality assurance, physical and mechanical test methods, chemical test methods and sampling and sample preparation.
Continue your reading with other pellet plant handbook post:
Pellet Plant Handbook : The History of Pellet Mill
Pellet Plant Handbook : ENplus Certification for Wood Pellet Plant
Pellet Plant Handbook : The Physical Characteristics of Wood Pellet
Pellet Plant Handbook : The Chemical Characteristics of Biomass Pellet
Pellet Plant Handbook : The Interdependencies Between Biomass Pellet Parameters
